Networking
Description of traffic flow for simple(no Istio) Single cluster traffic flow.
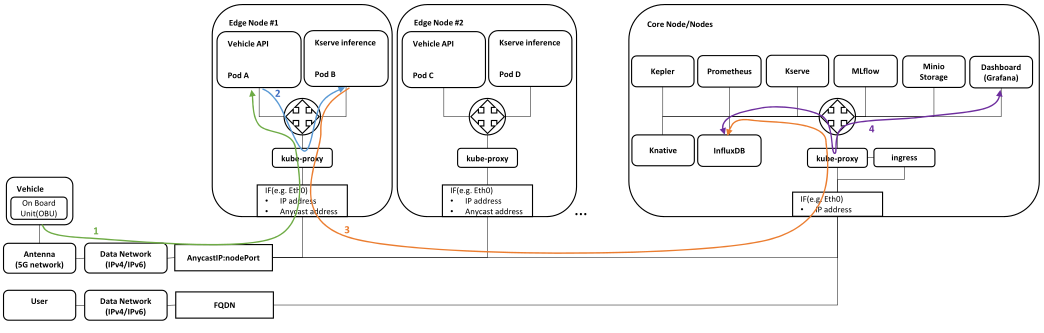
Vehicle data processing
 |
| Vehicle data processing |
Traffic flow:
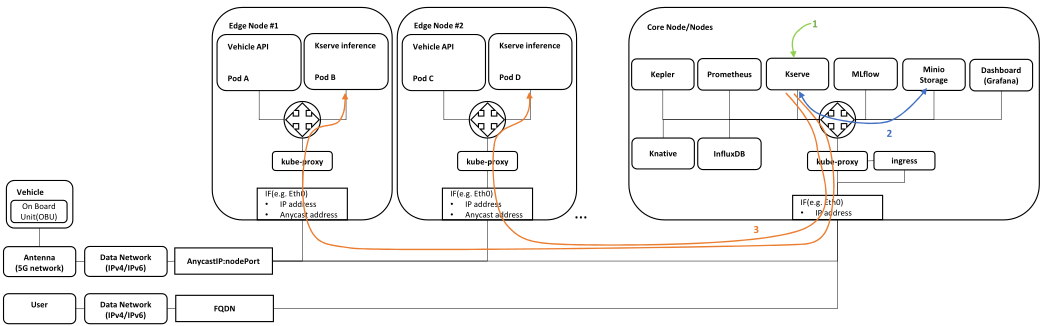
- Vehicle sends measurements to Vehicle API service (provided by Idneo – data preprocessing +Redis DB)
- transmission is received by antenna
- Transmission enters data(IPv4/IPv6) network
- Data is forwarded to the closest Kubernetes Edge node using (i) Anycast IP address, shared by all Edge Nodes, and (ii) nodePort defined in NodePort service
- Edge Node receives the data, checks the IP table in kube-proxy, and forwards it to local Pod A as the service is configured with
externalTrafficPolicy: Local
- If there is no local Pod for Vehicle API service, the packet is dropped
- Vehicle API service forwards the data to the ML prediction service(Kserve inference)
- Data is forwarded to Pod B as Kserve inference service is configured with
internalTrafficPolicy: Local
- If there is no local Pod for Kserve inference service, the packet is dropped
- or ML prediction service pod periodically queries local Redis DB in Vehicle API service – as Vehicle API service is also configured with
internalTrafficPolicy: Local
- If there is no local Pod for Vehicle API service, the queries/requests are dropped
- Kserve inference service pushes the data into InfluxDB
- Grafana periodically queries data from InfluxDB
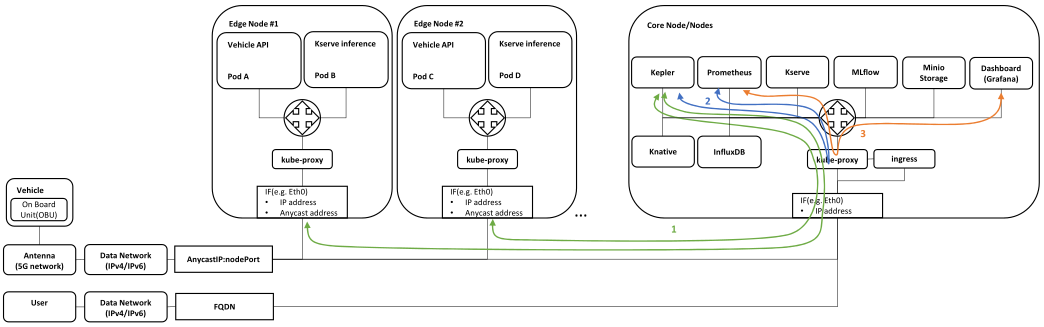
Energy consumption monitoring
 |
| Energy consumption monitoring |
Traffic flow:
- Kepler exporter uses eBPF to probe CPU, GPU, RAM performance counters and exposes them over time via HTTP
- Prometheus periodically queries Kepler exporter for a new data
- Grafana periodically queries Prometheus for anew data
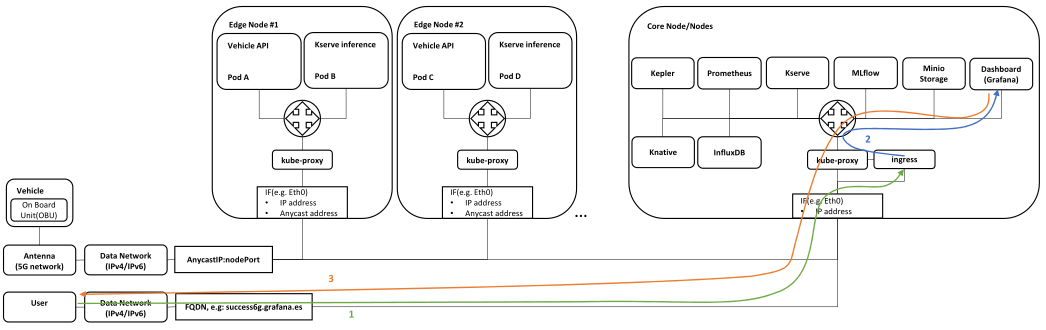
Vehicle data and energy consumption monitoring
 |
| Vehicle data and energy consumption monitoring |
Traffic flow:
- User enters Grafana FQDN in the web browser and is forwarded to the Ingress controller
- Ingress controller translates the FQDN to the appropriate service and forwards it
- Grafana GUI comes up in the Users web browser
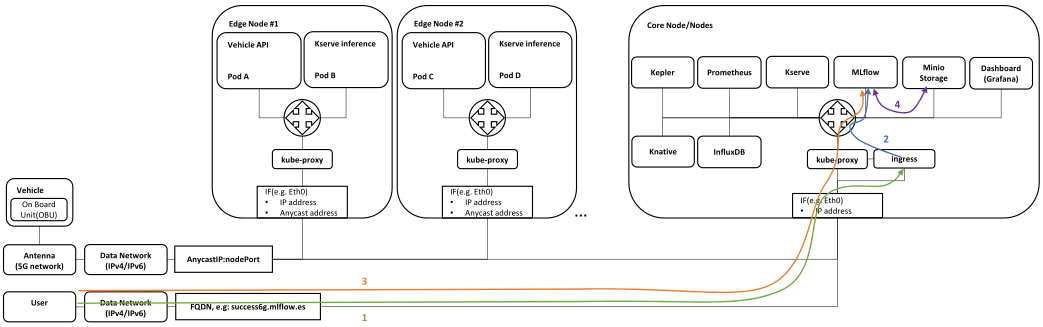
ML model development/update
 |
| ML model development/update |
Traffic flow:
- User enters MLflow FQDN in the web browser and is forwarded to the Ingress controller
- Ingress controller translates the FQDN to the appropriate service and forwards it to Mlflow GUI where user can check current models
- User updates the model locally or in cloud and uploads it to MLflow API
- Mlflow API forwards the model to the backend database - Minio
ML model deployment
 |
| ML model deployment |
Traffic flow:
- Admin user instructs Kserve to deploy a model
- Kserve queries the model from Minio storage
- Kserve updates/”serves” the model in all Kserver inference Pods




